6. Login
In this section, I’ll explain how I made the login function. This project is designed as a single-user program. In other words, only the administrator is authorized to access and operate the system. Therefore, I created a single account with the ID: “admin”.
1. The design of the login function
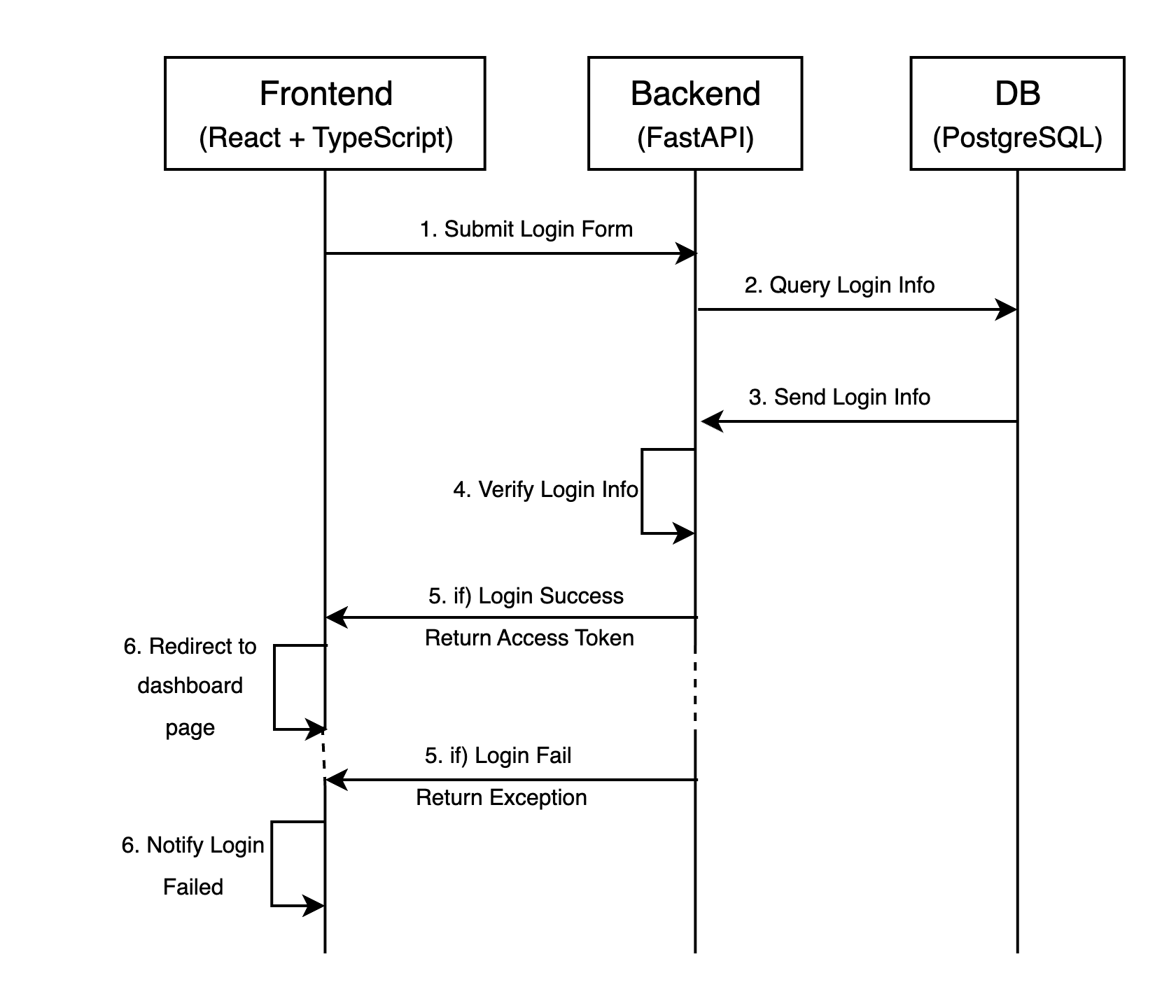
1.1 Diagram
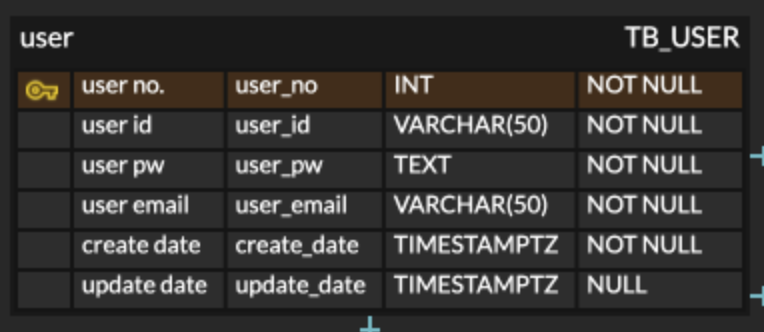
1.2 ERD
-
TB_USERcontains no., id, password, email, created date, and updated date.- user_no: Unique numeric identifier for the user
- user_id: The login ID (username)
- user_pw: Encrypted password
- user_email: Registered email address
- create_date: Timestamp when the account was created
- update_date: Timestamp when the account was last updated
2. Backend
2.1 DB Model
-
To create the user table in the database, I needed to define a user model.
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, Text, DateTime, func from sqlalchemy.schema import Sequence from core import Database user_no_seq = Sequence('user_no_seq', start=10001) # Start user_no from 10001 class User(Database.get_base()): """User model for the application.""" __tablename__ = 'tb_user' user_no = Column(Integer, user_no_seq, primary_key=True, server_default=user_no_seq.next_value()) user_id = Column(String(50), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True) user_pw = Column(Text, nullable=False) user_email = Column(String(50), unique=True, nullable=False) create_date = Column(DateTime(timezone=True), server_default=func.now(), nullable=False) update_date = Column(DateTime(timezone=True), onupdate=func.now()) def __repr__(self): return f"<User(id={self.user_id}, email={self.user_email})>"- To set 10001 as starting number of the user no., I used the
Sequenceclass from SQLAlchemy.
- To set 10001 as starting number of the user no., I used the
2.2 Password Encryption & Verification
-
I used
bcryptfor secure password hashing.from passlib.context import CryptContext # Password hashing context using bcrypt pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto") # --- Password Hashing --- def hash_password(password: str) -> str: """Hash a password using bcrypt.""" return pwd_context.hash(password) -
For verification of the hashed password, I wrote the following code.
def verify_password(plain_password: str, hashed_password: str) -> bool: """Verify a plain password against the hashed password.""" return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
2.3 Initialize User Table
-
To initialize the user table, I created a function that checks for the existence of the admin user and inserts it if not found. The function also ensures that the user sequence is properly synced.
def initialize_database(): ... try: existing_user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id='admin').first() if not existing_user: admin = User( user_no=10001, user_id = "admin", user_email = "{ADMIN_EMAIL}", user_pw = hash_password("{ADMIN_PASSWORD}") ) session.add(admin) session.commit() session.execute(text("SELECT setval('user_no_seq', 10001, true)")) session.commit() logger.info("Admin user created successfully.") else: logger.info("Admin user already exists.") except IntegrityError as e: session.rollback() logger.error(f"IntegrityError during admin user initialization: {e}") except Exception as e: session.rollback() logger.error(f"Error during database initialization: {e}") finally: session.close()
2.4 User Service
-
To authenticate a user, I implemented an authentication method in the UserService class.
class UserService: ... def authenticate_user(self, user_id: str, user_pw: str) -> User | None: """Authenticate a user by ID and password.""" user = self.get_user_by_id(user_id) if user and verify_password(user_pw, user.user_pw): return user return None
2.5 JWT Token Creation & Verification
-
Note: The current JWT implementation lacks features such as token revocation, refresh tokens, and IP/device-based validation. These will be addressed in future updates to enhance overall security.
-
First, this is the creation code of the JWT token.
from jose import jwt, JWTError, ExpiredSignatureError from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone # --- JWT Token Generation --- def create_jwt_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Optional[timedelta] = None) -> str: """Create a JWT token with an expiration time.""" to_encode = data.copy() now = datetime.now(timezone.utc) expire = now + (expires_delta or timedelta(...)) to_encode.update({ "sub": data["user_id"], "iat": now, "exp": expire }) encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, settings.SECRET_KEY, algorithm=settings.JWT_ALGORITHM) return encoded_jwt -
Lastly, this is the verification code of the JWT token.
def verify_jwt_token(token: str) -> dict: """Verify a JWT token and return the payload.""" try: payload = jwt.decode( token, settings.SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[settings.JWT_ALGORITHM], options={"verify_aud": False}, ) return payload except ExpiredSignatureError: raise ValueError("Token has expired") except JWTError: raise ValueError("Invalid token") except Exception as e: raise ValueError(f"Token verification failed: {str(e)}")
2.6 Login DTO
-
For stability, I’m using DTO for data transfer.
from pydantic import BaseModel # Request DTOs class LoginRequest(BaseModel): user_id: str user_pw: str # Response DTOs class LoginResponse(BaseModel): access_token: str token_type: str = "bearer"
2.7 Login API
-
This API receives a login form from the frontend. This proceeds the authentication if a user tries to log in.
-
If the login is successful, the API returns a JWT token to the frontend; otherwise, it raises an appropriate exception.
@user_router.post("/login", response_model=LoginResponse) def login(request: LoginRequest, db: Session = Depends(get_db)): try: user_service = UserService(db) user = user_service.authenticate_user(request.user_id, request.user_pw) if not user: logger.warning(f"Login failed: invalid credentials for user_id '{request.user_id}'") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Invalid credentials" ) token = create_jwt_token({"user_id": user.user_id}) logger.info(f"Token issued for user_id: {user.user_id}") return LoginResponse(access_token=token) except ValidationError as ve: logger.error(f"Validation error: {ve}") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_422_UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY, detail="Invalid request format" ) except HTTPException as he: logger.warning(f"HTTPException raised: {he.detail}") raise he except Exception as e: logger.exception("Unexpected error during login") raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Internal server error")
3. Frontend
3.1 main.tsx
-
I needed to change the initial react codes.
import ... createRoot(document.getElementById('root')!).render( <StrictMode> <BrowserRouter> <App /> </BrowserRouter> </StrictMode>, )
3.2 App.tsx
-
Also, I had to modify the initial React setup.
-
And, I set the routes for the ‘dashboard’ and ’login’ pages.
import ... function App() { return ( <Routes> <Route path="/" element={<Root />} /> <Route path="/dashboard" element={<Dashboard />} /> <Route path="/login" element={<Login />} /> </Routes> ) } export default App
3.3 Dashboard.tsx
-
I created this page for the dashboard, but in this time I simply added text to represent the ‘dashboard’ page.
-
I made this file in the ‘/src/pages’ directory.
import { useEffect } from "react"; const Dashboard = () => { useEffect(() => { console.log("Dashboard component mounted"); }, []); return ( <div> <h1>Dashboard</h1> <p>Welcome to the dashboard!</p> </div> ); } export default Dashboard;
3.4 axios.ts
-
I created this code for convenient using for API communications.
-
I made this file in the ‘/src/services’ directory.
import axios from 'axios'; const api = axios.create({ baseURL: '/api', // Adjust this if your API base URL is different }); export default api;
3.5 Login.tsx
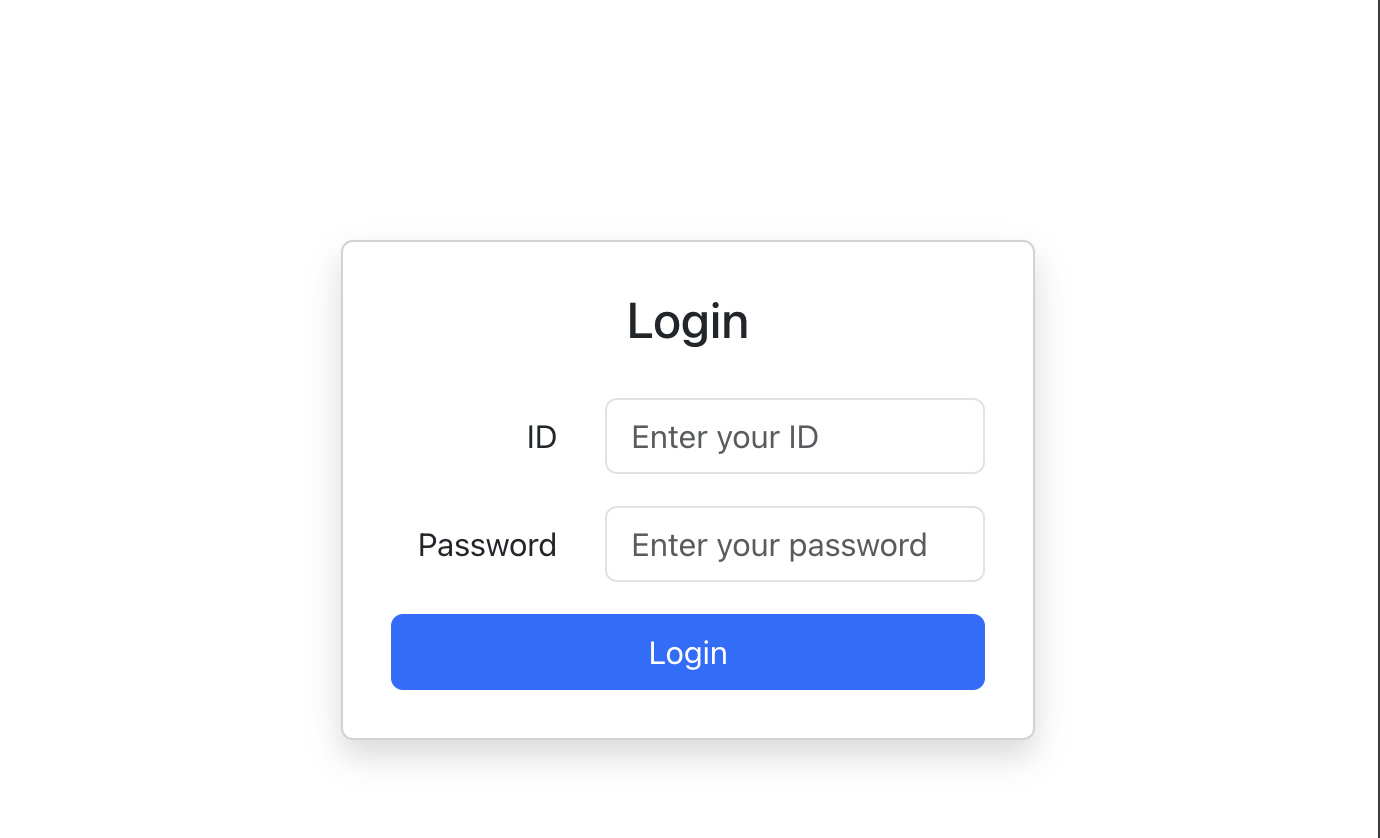
-
This is the Login page.
-
When a user tries to log in, this frontend sends the login form to the backend using RESTful.
-
If the user logs in successfuly, this page receives an access token in the response from the backend, and then saves the token in localStorage.
-
I made this file in the ‘/src/pages’ directory.
import { useState, useEffect } from "react"; import { useNavigate } from "react-router"; import { Form, Button, Card, Alert, Container,Col, Row } from "react-bootstrap"; import api from "@/services/axios"; const Login = () => { const navigate = useNavigate(); // input states const [id, setId] = useState(""); const [password, setPassword] = useState(""); // error state const [error, setError] = useState(""); // mount log for debugging useEffect(() => { console.log("Login component mounted"); }, []); const handleSubmit = async (e: React.FormEvent) => { e.preventDefault(); setError(""); // Reset error state try { // Make a POST request to the login endpoint const response = await api.post("/users/login", { user_id: id, user_pw: password }); // If login is successful, store the token and redirect localStorage.setItem("access_token", response.data.access_token); navigate("/dashboard"); } catch (err) { // Handle errors (e.g., invalid credentials) console.error("Login error:", err); // Set error message based on the error response setError("Login failed. Please check your credentials."); } }; return ( <Container className="d-flex justify-content-center align-items-center" style={{ minHeight: "100vh" }}> <Card style={{ width: "100%", maxWidth: "500px" }} className="p-4 shadow"> <h3 className="mb-4 text-center">Login</h3> <Form onSubmit={handleSubmit}> <Form.Group as={Row} className="mb-3" controlId="formId"> <Form.Label column sm="4" className="text-end">ID</Form.Label> <Col sm="8"> <Form.Control type="text" value={id} onChange={(e) => setId(e.target.value)} placeholder="Enter your ID" required /> </Col> </Form.Group> <Form.Group as={Row} className="mb-3" controlId="formPassword"> <Form.Label column sm="4" className="text-end">Password</Form.Label> <Col sm="8"> <Form.Control type="password" value={password} onChange={(e) => setPassword(e.target.value)} placeholder="Enter your password" required /> </Col> </Form.Group> {error && <Alert variant="danger">{error}</Alert>} <Button variant="primary" type="submit" className="w-100"> Login </Button> </Form> </Card> </Container> ); }; export default Login;
3.6 Root.tsx
-
I didn’t need to assign the root page to any specific functionality. So I set redirection to the dashboard and the login pages. If the token is not set, the page will be redirected to the login page.
-
I made this file in the ‘/src/pages’ directory.
import { useEffect } from "react"; import { useNavigate } from "react-router"; const Root = () => { const navigate = useNavigate(); useEffect(() => { const token = localStorage.getItem("access_token"); if (!token) { // If no token is found, redirect to the login page navigate("/login"); } else { // If a token is found, redirect to the dashboard navigate("/dashboard"); } }, [navigate]); return null; // This component does not render anything itself }; export default Root;
4. Result
5. Future Improvements
Although the current login system works as intented for a single-admin use case, there are several improvements I plan to implement in the future.
5.1 Security Enhancements
- Adjust Token Lifespan
- I need to determine the appropriate lifespan for the access token. Further research and testing are required to balance usability and security.
- Limit Login Attemps
- Prevent brute-force attacks by limiting the number of failed login attempts per IP or user, and by applying a temporary lockout or cool-down period after repeated failures.
- Add CSRF/XSS Protections
- Improve frontend security by enforcing CSRF token checks (especially if cookie-based auth is introduced) and sanitizing user input to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.