8. Login Log
In this section, I’ll explain how I implemented the login log functionality. Since this is a single-user application, logging each login might seem unnecessary at first. However, I decided to build this feature to enhance security and maintain visibility over all login activities. Recording login attempts allows me to track unauthorized access or unexpected behavior in the system.
1. The design of the login log function
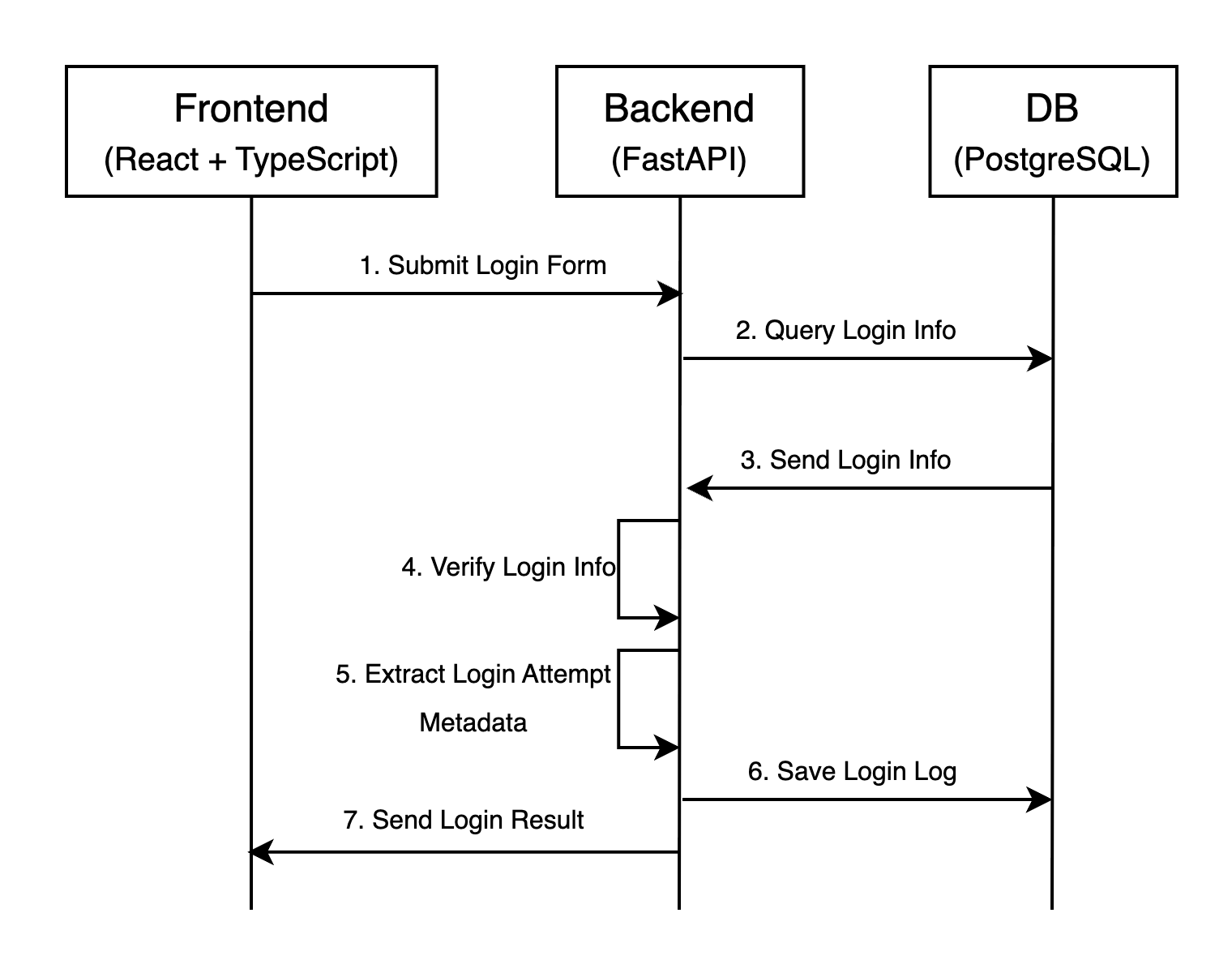
1.1 Diagram
-
The diagram below illustrates the communication flow between the frontend, backend, and Database during a login process.
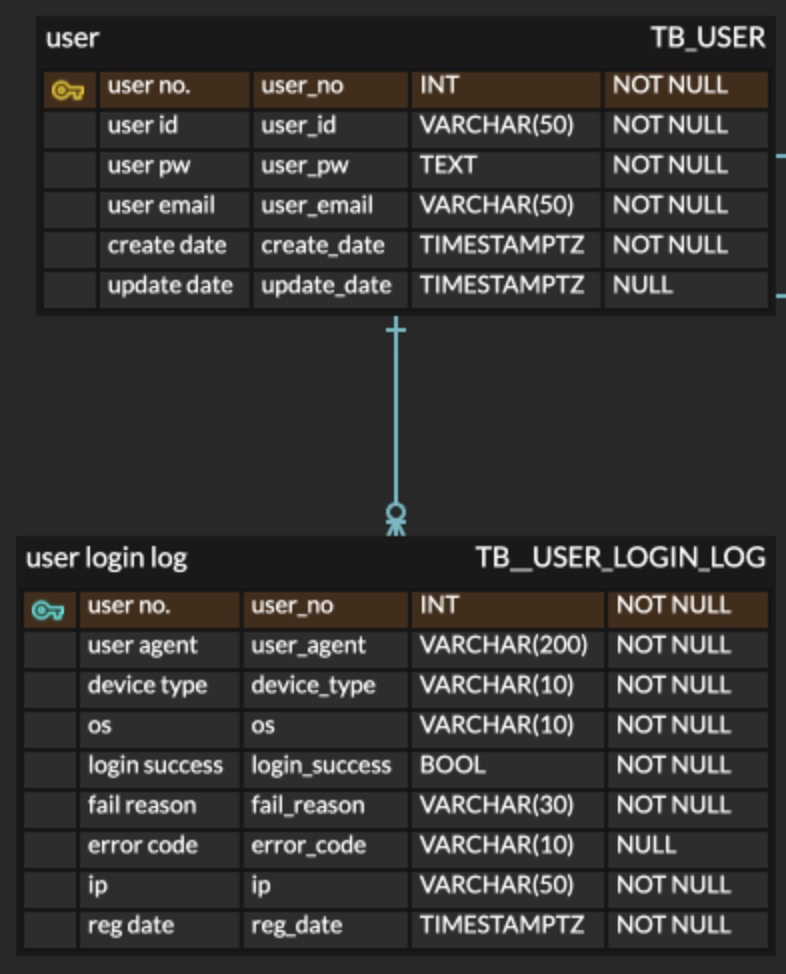
1.2 ERD
-
The following ERD shows the relationship between the
TB_USERandTB_USER_LOGIN_LOGtables. -
The
TB_USER_LOGIN_LOGtable records metadata for every login attempt.user_no: Foreign key referencing the useruser_agent,device_type,os: Extracted from the request headersip: IP address of the clientlogin_success: Whether the login attempt was successfulfail_reason,error_code: Used for debugging or anomaly detectionreg_date: Timestamp of the login attempt
2. Backend
2.1 DB Model
-
To persist the user login logs in the database, I defined the following SQLAlchemy model:
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, Boolean, DateTime, ForeignKey from sqlalchemy.sql import func from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship from core import Database class UserLoginLog(Database.get_base()): """User login log model for the application.""" __tablename__ = 'tb_user_login_log' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) user_no = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('tb_users.user_no'), nullable=False) user_agent = Column(String(255), nullable=False) device_type = Column(String(50), nullable=False) os = Column(String(10), nullable=False) login_success = Column(Boolean, nullable=False) fail_reason = Column(String(255), nullable=True) error_code = Column(String(10), nullable=True) ip= Column(String(50), nullable=False) reg_date = Column(DateTime(timezone=True), server_default=func.now(), nullable=False) user = relationship("User", backref="login_logs") def __repr__(self): return (f"<UserLoginLog(user_no={self.user_no}, " f"success={self.login_success}, ip={self.ip}, " f"reg_date={self.reg_date})>")
2.2 Enums
-
To maintain consistency in log data, I defined several enums Python’s enum module:
from enum import Enum
2.2.1 Device Type
-
Device type extracted from the User-Agent
class DeviceType(str, Enum): PC = "PC" MOBILE = "MOBILE" TABLET = "TABLET"
2.2.2 OS
-
Operating system classification
class OS(str, Enum): WINDOWS = "Windows" MACOS = "macOS" LINUX = "Linux" ANDROID = "Android" IOS = "iOS"
2.2.3 Login Fail Reason
-
Reasons for login failure, used for auditing or user feedback
class LoginFailReason(str, Enum): INVALID_CREDENTIALS = "Invalid credentials" ACCOUNT_LOCKED = "Account locked" ACCOUNT_DISABLED = "Account disabled" PASSWORD_EXPIRED = "Password expired" MFA_REQUIRED = "Multi-factor authentication required" MFA_FAILED = "Multi-factor authentication failed" UNKNOWN_ERROR = "Unknown error"
2.2.4 Error Code
-
Standardized error codes mapped to HTTP-like semantics
class ErrorCode(str, Enum): INVALID_REQUEST = "E400" UNAUTHORIZED = "E401" FORBIDDEN = "E403" NOT_FOUND = "E404" INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = "E500" SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = "E503"
2.3 UserLoginLogService
-
This service class is responsible for managing user login logs.
-
It is initialized with a SQLAlchemy database session(
Session).from sqlalchemy.orm import Session class UserLoginLogService: def __init__(self, db: Session): self.db = db
2.3.1 _extract_log_data method
-
A private method that extracts user login metadata from the request, including device type, OS, IP address, and login result.
from user_agents import parse as parse_user_agent from fastapi import Request from core import DeviceType, OS, LoginFailReason, ErrorCode class UserLoginLogService: ... def _extract_log_data( self, request: Request, user_no: int, login_success: bool, fail_reason: str = None, error_code: str = None) -> dict: """Extract log data from the request and parameters.""" user_agent_str = request.headers.get("User-Agent", "") ua = parse_user_agent(user_agent_str) # Determine the device type from the parsed User-Agent if ua.is_mobile: device_type = DeviceType.MOBILE elif ua.is_tablet: device_type = DeviceType.TABLET elif ua.is_pc: device_type = DeviceType.PC else: device_type = DeviceType.PC # Extract OS family from User-Agent os_family = ua.os.family.lower() if "windows" in os_family: os_name = OS.WINDOWS elif "mac" in os_family: os_name = OS.MACOS elif "linux" in os_family: os_name = OS.LINUX elif "android" in os_family: os_name = OS.ANDROID elif "ios" in os_family: os_name = OS.IOS else: os_name = OS.LINUX # Get client IP address from FastAPI request ip_address = request.client.host if request.client else "0.0.0.0" return { "user_no": user_no, "user_agent": user_agent_str[:255], "device_type": device_type, "os": os_name, "login_success": login_success, "fail_reason": fail_reason, "error_code": error_code, "ip": ip_address[:50] } -
This is an example of the return from this method:
# Returns: # { # "user_no": 10001, # "user_agent": "Mozilla/5.0 ...", # "device_type": "PC", # "os": "macOS", # "login_success": True, # "fail_reason": None, # "error_code": None, # "ip": "172.19.0.8" # }
2.3.2 create_log method
-
This method is responsible for creating and storing a new login log entry in the database.
-
It uses
_extract_log_data()to parse metadata from the request and wraps the DB transaction with proper error handling.... from models import UserLoginLog class UserLoginLogService: ... # Safely create and persist a new login log entry def create_log( self, request: Request, user_no: int, login_success: bool, fail_reason: LoginFailReason = None, error_code: ErrorCode = None ) -> UserLoginLog: """Create a new user login log entry.""" try: log_data = self._extract_log_data( request=request, user_no=user_no, login_success=login_success, fail_reason=fail_reason, error_code=error_code ) log_entry = UserLoginLog(**log_data) self.db.add(log_entry) self.db.commit() self.db.refresh(log_entry) return log_entry except Exception as e: self.db.rollback() logger.error(f"Failed to create login log: {e}") raise
2.4 log_login_attempt method
-
This is a wrapper method that receives login attempt information and delegates the actual creation to
create_log(). -
It ensures that a valid
user_nois present before logging to avoid null foreign key issues.... class UserLoginLogService: ... def log_login_attempt( self, request: Request, user_no: int, login_success: bool, fail_reason: LoginFailReason | None = None, error_code: ErrorCode | None = None ) -> None: # Skip logging if user_no is not provided (e.g., failed lookup) if user_no is None: logger.warning("Skipping login log creation due to missing user_no.") return self.create_log( request=request, user_no=user_no, login_success=login_success, fail_reason=fail_reason, error_code=error_code )
3. UserService
-
This section shows how
UserLoginLogServiceis integrated into theUserService.class UserService: ... def authenticate_user(self, user_id: str, user_pw: str) -> User: ... if not user or not verify_password(user_pw, user.user_pw): logger.warning(f"Authentication failed for user_id='{user_id}'") user_no = user.user_no if user else None # User Login Log Service self.login_log_service.log_login_attempt( request=self.request, user_no=user_no, login_success=False, fail_reason=LoginFailReason.INVALID_CREDENTIALS, error_code=ErrorCode.UNAUTHORIZED ) raise InvalidCredentialsException() # User Login Log Service self.login_log_service.log_login_attempt( request=self.request, user_no=user.user_no, login_success=True ) logger.info(f"Authentication successful for user_id='{user.user_id}'") return user
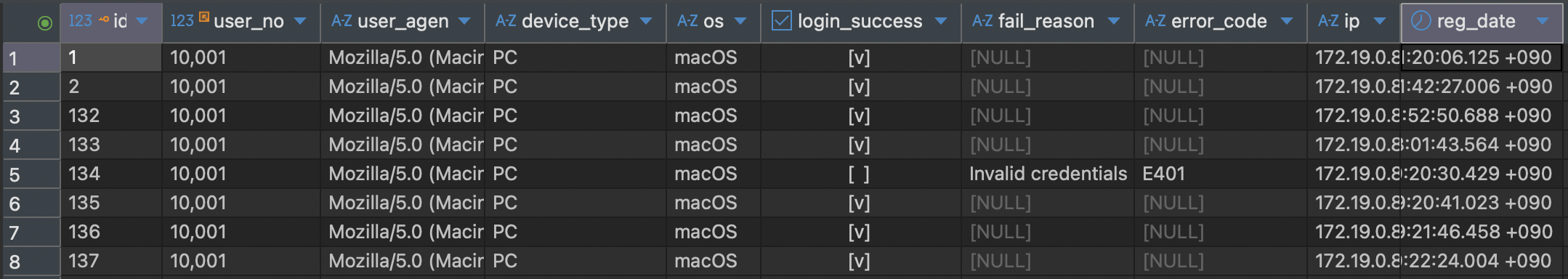
4. Result
-
The following is a snapshot of login log records stored in the
tb_user_login_logtable. -
It demonstrates how metadata is captured for each login attempt, including success/failure, user agent, OS, and IP address.
-
This log format helps monitor both successful and failed login attempts, enabling anamoly detection and auditing.