10. Managing API Keys - Backend Implementation
Managing API Keys from multiple exchanges requires both exchange metadata management and secure key storage. In this post, I describe the database schema and service logic used to support this.
1. The Design of the API Key Management System
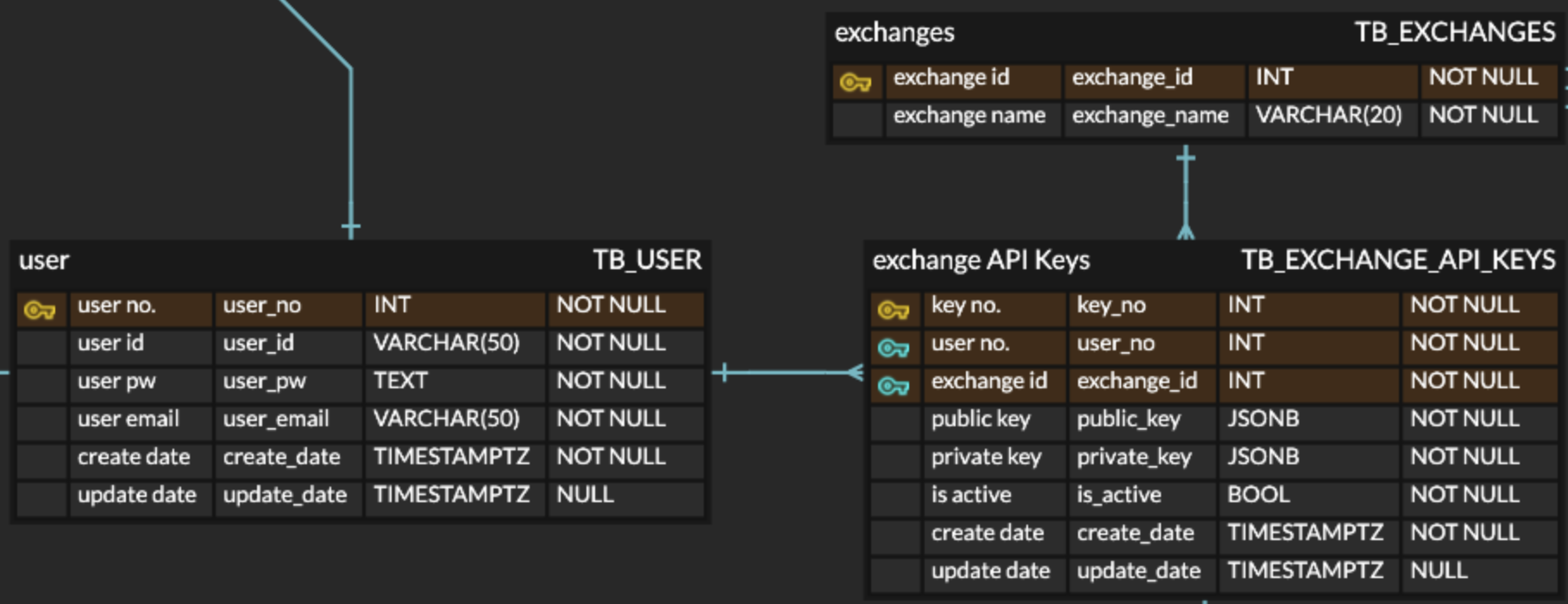
1.1 ERD
-
The functionality is based on three relational tables:
TB_USER,TB_EXCHANGES, andTB_EXCHANGE_API_KEYS. -
TB_EXCHANGESstores registered exchanges.exchange_id: Unique exchange identifierexchange_name: Name of the exchange
-
TB_EXCHANGE_API_KEYSmanages the API keys linked to exchanges per user.key_no: Primary key for this tableuser_no: Foreign Key referencingTB_USERexchange_id: Foreign key referencingTB_EXCHANGESpublic_key: Public-facing key (e.g., Access Key)private_key: Private key (e.g., Secret Key)is_active: Whether this API key is activecreate_date: Timestamp when the key was createdupdate_date: Timestamp of the last update
-
Relationships
- A user can register multiple API keys for different exchanges.
- Each key must reference a valid exchange and user.
- This structure supports a multi-exchange trading system.
2. Backend
2.1 DB Models
2.1.1 Exchanges Model
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String
from sqlalchemy.schema import Sequence
from core import Database
exchange_no_seq = Sequence('exchange_no_seq', start=101)
class Exchanges(Database.get_base()):
"""Exchange model for the application"""
__tablename__ = 'tb_exchanges'
exchange_id = Column(Integer, exchange_no_seq, primary_key=True, server_default=exchange_no_seq.next_value())
exchange_name = Column(String(20), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Exchange(no={self.exchange_id}, name={self.exchange_name})>"- exchange_no_seq ensures a custom sequence starting from 101 for exchange_id.
2.1.2 ExchangeAPIKeys
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, Boolean, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint, DateTime
from sqlalchemy.dialects.postgresql import JSONB
from sqlalchemy.sql import func
from core import Database
class ExchangeAPIKeys(Database.get_base()):
"""Exchange API Keys model for the application"""
__tablename__ = "tb_exchange_api_keys"
key_no = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
user_no = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("tb_users.user_no"), nullable=False)
exchange_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("tb_exchanges.exchange_id"), nullable=False)
public_key = Column(JSONB, nullable=False)
private_key = Column(JSONB, nullable=False)
is_active = Column(Boolean, nullable=False, default=True)
create_date = Column(DateTime(timezone=True), server_default=func.now(), nullable=False)
update_date = Column(DateTime(timezone=True), onupdate=func.now(), nullable=True)
__table_args__ = (
UniqueConstraint("user_no", "exchange_id", name="uq_user_exchange"),
)- A composite unique constraint ensures that each user can register only one API key per exchange.
2.2 Exchange Table Initialization
-
The following function inserts the default exchange (Coinone) into the database if it doesn’t exist:
def initialize_default_exchange(session): try: existing_exchange = session.query(Exchanges).filter_by(exchange_id=101).first() if not existing_exchange: default_exchange = Exchanges( exchange_id=101, exchange_name="Coinone" ) session.add(default_exchange) session.commit() session.execute(text("SELECT setval('exchange_no_seq', 101, true)")) session.commit() logger.info("Default exchange 'Coinone' created successfully.") else: logger.info("Default exchange 'Coinone' already exists.") except IntegrityError as e: session.rollback() logger.error(f"IntegrityError during exchange initialization: {e}") except Exception as e: session.rollback() logger.error(f"Error during exchange initialization: {e}")
2.3 ExchangesService
- This service layer encapsulates all logic related to exchange management.
2.3.1 Initialization
-
The
__init__method initializes the DB session for service use.from sqlalchemy.orm import Session class ExchangesService: """Service class for exchanges-related operations.""" def __init__(self, db: Session): self.db = db
2.3.2 create_exchange()
-
Creates a new exchange entry in the database.
-
Handles duplicate insert attempts via IntegrityError
... from sqlalchemy.exc import IntegrityError from models import Exchanges from loguru import logger class ExchangesService: ... def create_exchange(self, exchange_name: str) -> Exchanges: """Create a new exchange.""" try: logger.info(f"Accepting to create exchange: {exchange_name}") new_exchange = Exchanges(exchange_name=exchange_name) self.db.add(new_exchange) self.db.commit() self.db.refresh(new_exchange) logger.info(f"Exchange created successfully: exchange_id={new_exchange.exchange_id}, name={exchange_name}") return new_exchange except IntegrityError as e: self.db.rollback() if 'UNIQUE constraint' in str(e.orig): logger.warning(f"Duplicate exchange creation attempted: exchange_name={exchange_name}") raise ValueError(f"Exchange with name '{exchange_name}' already exists.") from e else: logger.error(f"IntegrityError during exchange creation: {str(e.orig)}") raise ValueError(f"Failed to create exchange due to database integrity error.") from e
2.3.3 get_all_exchanges()
-
Fetches all registered exchanges from the table, orderd by exchange_id.
... from models import Exchanges from loguru import logger class ExchangesService: ... def get_all_exchanges(self): """Retrieve all registered exchanges""" logger.info(f"Retrieving all exchanges.") try: exchanges = ( self.db.query(Exchanges) .order_by(Exchanges.exchange_id.asc()) .all() ) logger.info(f"Retrieved {len(exchanges)} exchanges.") return exchanges except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to retrieve exchanges: {str(e)}") raise ValueError("Failed to retrieve exchanges from the database.") from e
2.4 ExchangeAPIKeyService
- This service layer encapsulates all logic related to secure management of user exchange API keys, including encryption, duplication checks, and masked key exposure.
2.4.1 Initialization
-
The constructor initializes both the DB session and a symmetric encryption key.
-
The encrytion key is loaded from an
.envvariable and decoded usingbase64.from sqlalchemy.orm import Session from core import settings class ExchangeAPIKeyService: def __init__(self, db: Session): self.db = db self.secret_key = settings.symmetric_key_bytes -
Example
.envconfiguration:SYMMETRIC_KEY={your_base64_encoded_key} -
Settingsaccessor for decoded byte key:... import base64 class Settings(BaseSettings): ... SYMMETRIC_KEY: str ... @property def symmetric_key_bytes(self) -> bytes: return base64.b64decode(self.SYMMETRIC_KEY)
2.4.2 AES-GCM Encryption/Decryption
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import base64
def encrypt_data(plain_text: str, key: bytes) -> dict:
"""Encrypt data using AES-GCM."""
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_GCM)
ciphertext, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(plain_text.encode('utf-8'))
return {
"enc": base64.b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8'),
"nonce": base64.b64encode(cipher.nonce).decode('utf-8'),
"tag": base64.b64encode(tag).decode('utf-8'),
"alg": "AES-GCM",
"version": 1
}
def decrypt_data(enc_data: dict, key: bytes) -> str:
"""Decrypt data using AES-GCM."""
ciphertext = base64.b64decode(enc_data["enc"])
nonce = base64.b64decode(enc_data["nonce"])
tag = base64.b64decode(enc_data["tag"])
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=nonce)
plain_text = cipher.decrypt_and_verify(ciphertext, tag)
return plain_text.decode('utf-8')2.4.3 create_api_key()
-
Validates inputs, checks for duplicates, encrypts the keys, and stores them securely.
... from models import ExchangeAPIKeys from core import encrypt_data, decrypt_data, settings from loguru import logger from dto import ExchangeAPIKeyRequest class ExchangeAPIKeyService: ... def create_api_key(self, body: ExchangeAPIKeyRequest) -> None: user_no = body.user_no exchange_id = body.exchange_id public_key = body.public_key private_key = body.private_key logger.info(f"Storing API key for user_no={user_no}, exchange_id={exchange_id}") existing = self.db.query(ExchangeAPIKeys).filter_by(user_no=user_no, exchange_id=exchange_id).first() if existing: raise ValueError(f"API key already exists for user_no={user_no}, exchange_id={exchange_id}") if not isinstance(public_key, str) or not isinstance(private_key, str): raise TypeError("Keys must be JSON-formatted strings") public_key_enc = encrypt_data(public_key, self.secret_key) private_key_enc = encrypt_data(private_key, self.secret_key) record = ExchangeAPIKeys( user_no=user_no, exchange_id=exchange_id, public_key=public_key_enc, private_key=private_key_enc ) try: self.db.add(record) self.db.commit() self.db.refresh(record) except Exception as e: self.db.rollback() logger.error(f"Failed to store API key: {e}") raise
2.4.4 get_all_masked_api_keys()
-
Returns decrypted and masked API keys for frontend display (e.g., abcd****efgh).
from typing import List from sqlalchemy.orm import Session from models import ExchangeAPIKeys, Exchanges from core import encrypt_data, decrypt_data, settings from loguru import logger from dto import ExchangeAPIKeyRequest, ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse class ExchangeAPIKeyService: ... def get_all_masked_api_keys(self, user_no: int) -> List[ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse]: logger.info(f"Retrieving all API keys for user_no={user_no}") records = ( self.db.query(ExchangeAPIKeys) .filter_by(user_no=user_no) .all() ) masked_list = [] for record in records: try: public_key = decrypt_data(record.public_key, self.secret_key) private_key = decrypt_data(record.private_key, self.secret_key) exchange = self.db.query(Exchanges).filter_by(exchange_id=record.exchange_id).first() if not exchange: logger.warning(f"Exchange not found: id={record.exchange_id}") continue masked = ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse( exchange_id=record.exchange_id, exchange_name=exchange.exchange_name, public_key_masked=public_key[:4] + "****" + public_key[-4:], private_key_masked=private_key[:4] + "****" + private_key[-4:], update_date=record.update_date, is_active=record.is_active, ) masked_list.append(masked) except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to process API key for record id={record.key_no}: {e}") return masked_list
2.5 DTOs
2.5.1 Exchanges DTO
from pydantic import BaseModel
class ExchangesRequest(BaseModel):
exchange_name: str
class ExchangesResponse(BaseModel):
exchange_id: int
exchange_name: str
model_config = {
"from_attributes": True
}2.5.2 Exchange API Key DTO
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional
from datetime import datetime
class ExchangeAPIKeyRequest(BaseModel):
user_no: int
exchange_id: int
public_key: str
private_key: str
# DTO for masked API key response
class ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse(BaseModel):
exchange_id: int
exchange_name: str
public_key_masked: str
private_key_masked: str
is_active: bool
update_date: Optional[datetime]
model_config = {
"from_attributes": True
}2.6 Settings Router
-
This router is for the Settings menu of the frontend. For this, I set this router’s prefix like this.
from fastapi import APIRouter, Depends, HTTPException, status from sqlalchemy.orm import Session from service import ExchangesService, ExchangeAPIKeyService, get_db from loguru import logger from dto import ExchangesResponse, ExchangesRequest, ExchangeAPIKeyRequest, ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse from typing import List settings_router = APIRouter(prefix="/api/settings", tags=["settings"])
2.6.1 fetch_all_exchanges()
-
This endpoint sends response with an exchange list.
settings_router = APIRouter(prefix="/api/settings", tags=["settings"]) @settings_router.get("/exchanges", response_model=List[ExchangesResponse], summary="All Registered Exchanges") def fetch_all_exchanges(db: Session = Depends(get_db)): logger.info(f"Fetching all registered exchanges") try: exchange_service = ExchangesService(db) exchanges = exchange_service.get_all_exchanges() return exchanges except Exception as e: logger.exception("Failed to fetch registered exchanges") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, detail="Unable to fetch registered exchanges" )
2.6.2 create_exchange()
-
This endpoint is for registering a new exchange.
@settings_router.post("/exchanges", response_model=List[ExchangesResponse], summary="Register New Exchange") def create_exchange(body: ExchangesRequest, db: Session = Depends(get_db)): exchange_name = body.exchange_name logger.info(f"Creating new exchange: {exchange_name}") try: exchange_service = ExchangesService(db) exchange_service.create_exchange(exchange_name) exchanges = exchange_service.get_all_exchanges() return exchanges except ValueError as ve: logger.warning(f"Validation failed: {ve}") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST, detail=str(ve) ) except Exception as e: logger.exception("Failed to create new exchange") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, detail="Unable to create new exchanges" )
2.6.3 register_exchange_api_key()
-
This endpoint is for registering a exchange API key.
@settings_router.post("/exchange-api-key", summary="Register Exchange API Key") def register_exchange_api_key(body: ExchangeAPIKeyRequest, db: Session = Depends(get_db)): logger.info(f"Registering exchange API key for user_no={body.user_no}, exchange_id={body.exchange_id}") try: service = ExchangeAPIKeyService(db) service.create_api_key(body) return {"message": "API key registered successfully."} except ValueError as ve: logger.warning(f"Validation failed: {ve}") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST, detail=str(ve) ) except Exception as e: logger.exception("Failed to register API key") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, detail="Unable to register API key" )
2.6.4 get_masked_api_keys()
-
This endpoint returns masked api key list.
@settings_router.get("/exchange-api-key", response_model=List[ExchangeAPIKeyMaskedResponse], summary="Get Masked API Key List") def get_masked_api_keys(user_no: int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)): logger.info(f"Retrieving masked API keys for user_no={user_no}") try: service = ExchangeAPIKeyService(db) return service.get_all_masked_api_keys(user_no) except Exception as e: logger.exception("Failed to retrieve masked API key list") raise HTTPException( status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, detail="Unable to fetch masked API keys" )
3. Conclusion
In this post, I covered the backend design for secure API key management in this project. The next post will walk through the frontend implementation.